The global transition towards renewable sources of energy has become an irreversible trend, spurred by concerns over climate change, environmental degradation, and the quest for energy security. As countries worldwide commit to reducing carbon emissions, renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydropower are increasingly seen as critical elements of a sustainable future. This essay explores the transition to renewable energy, its implications for traditional energy sectors, and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
The shift towards renewable energy
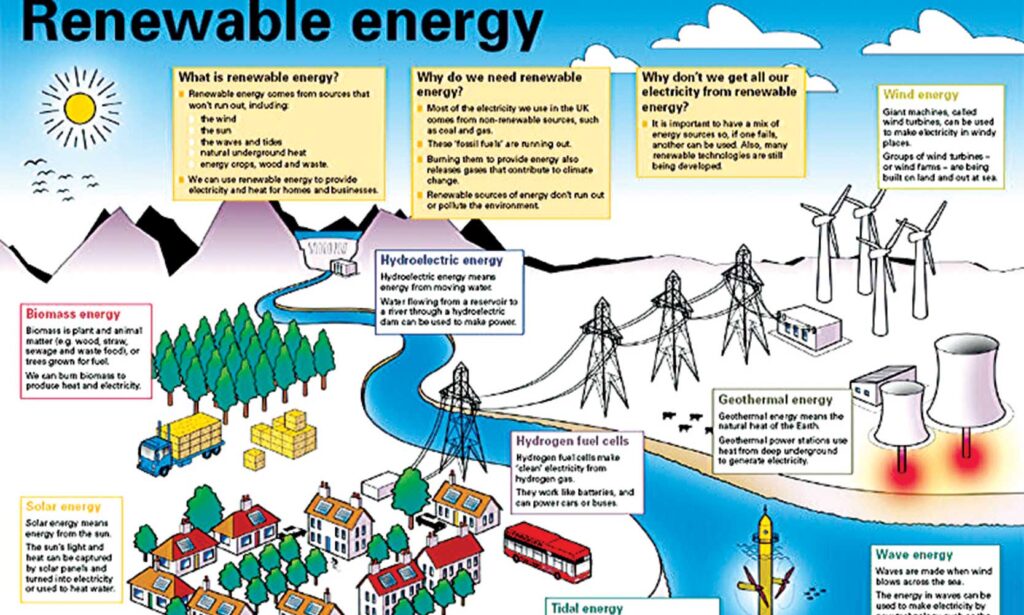
The adoption of renewable energy sources has been growing exponentially over the past few decades. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), renewables accounted for 80% of all new electricity generation in 2020, with solar and wind energy leading the charge (IRENA, 2021). This trend is expected to continue, driven by government policies, technological advancements, and falling costs. However, despite this rapid growth, renewable energy still represents a small fraction of the global energy mix, pointing to significant untapped potential.
Implications for the traditional energy sector
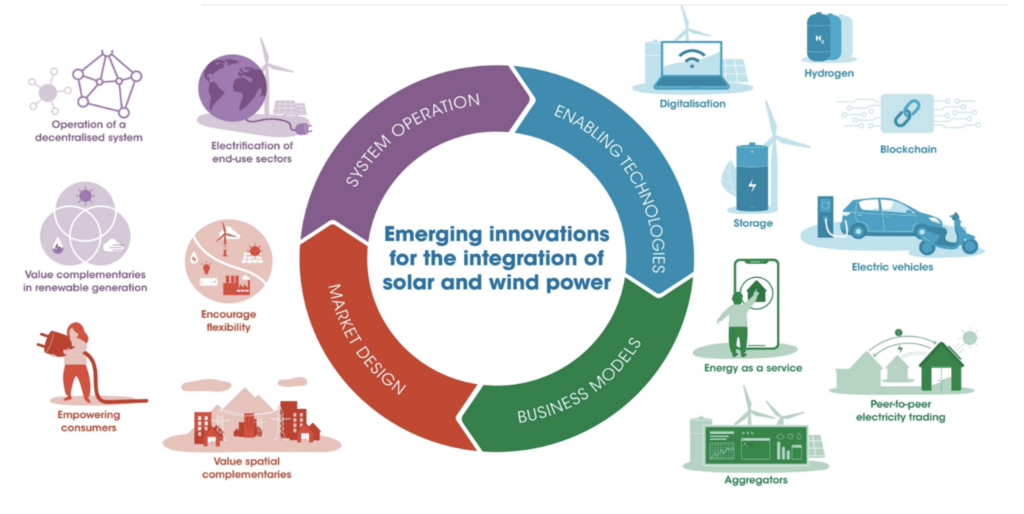
The increasing adoption of renewable energy has significant implications for the traditional energy sector. Most notably, it poses a threat to fossil fuel industries, including oil, gas, and coal. With the rise of electric vehicles, improvements in battery storage technology, and an increasing focus on energy efficiency, demand for fossil fuels is expected to decline in the coming decades. This transition could have far-reaching economic and geopolitical impacts, particularly for countries heavily reliant on fossil fuel exports.
Challenges to the transition
Despite the many benefits, transitioning to renewable energy is not without challenges. Firstly, renewables are intermittent by nature, which presents issues in terms of energy storage and grid reliability. Secondly, the production and disposal of renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels and batteries, can have significant environmental impacts. Lastly, the transition could lead to job losses in traditional energy sectors, requiring efforts to ensure a just transition for affected workers and communities.
Opportunities for innovation and economic growth
Despite these challenges, the transition to renewable energy offers numerous opportunities for innovation and economic growth. Renewable technologies are becoming increasingly cost-competitive, and their deployment could stimulate job creation and spur economic activity. Moreover, renewable energy can play a crucial role in addressing energy poverty, particularly in developing countries, where access to reliable, affordable energy can catalyse socio-economic development.
The role of policy and international cooperation
Successful transition to renewable energy will require supportive policy frameworks and international cooperation. Governments can play a vital role by implementing policies that incentivise renewable energy deployment, such as feed-in tariffs, renewable portfolio standards, and carbon pricing mechanisms. In addition, international cooperation can facilitate the sharing of best practices, technology transfer, and the mobilisation of financial resources to support renewable energy projects in developing countries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the transition to renewable energy represents a significant shift in our energy systems with profound implications for our economy, society, and environment. Despite the challenges, the benefits of renewable energy far outweigh the costs. With the right policies and international cooperation, the transition to renewable energy cannot only contribute to mitigating climate change but also open up new avenues for sustainable economic development. As the world grapples with the dual challenges of climate change and sustainable development, the transition to renewable energy will undoubtedly play a central role in shaping our shared future.
Reference:
- IRENA (2021). Renewable Capacity Statistics 2021. International Renewable Energy Agency.




