The curative power of music has come to light as a ray of hope amidst the immense body of medical knowledge. It has earned well-deserved acclaim as an efficient remedy for a variety of neurological and psychological problems, earning the name “music therapy”. The practice of music therapy is not a mere coincidence; rather, it is a highly specialised type of therapeutic intervention that deftly uses the emotive power of music and musical activities to meet the diverse physical, emotional, cognitive, and social requirements of individuals. Based on thorough study and empirical data, music therapy is an organised and evidence-based profession skilfully conducted by trained music therapists who skilfully use the language of music to accomplish significant therapeutic objectives. Melodies transform into instruments of healing and rebirth in their competent hands, orchestrating a symphony of recovery and resiliency in the lives of people they assist.
The effectiveness of music therapy has been seen in the improvement of cognitive function and the reduction of agitation in patients suffering from the suffocating grip of Alzheimer’s disease simply by enveloping them in the soothing embrace of familiar songs from their past.
The connection between music and the brain is a complicated and intriguing area of research. Music is a multimodal experience that stimulates multiple sections of the brain. Multiple brain regions, including the limbic system, motor cortex, and auditory cortex, have been found to be engaged while we listen to music by neuroimaging research. There may be an improvement in cognitive performance, an increase in creativity, and a sharpened concentration as a result of this extensive brain activity. Notably, the “Mozart effect,” which suggests transient increases in spatial-temporal cognition, has been linked to various genres of music, including classical compositions.
Music therapy has a long history dating back to ancient civilisations when music was discovered for its healing effects. However, music therapy as a legitimate profession began to develop during and after World War II when artists went to hospitals to perform for injured soldiers. The field has developed over time and is now acknowledged as an effective therapeutic strategy.
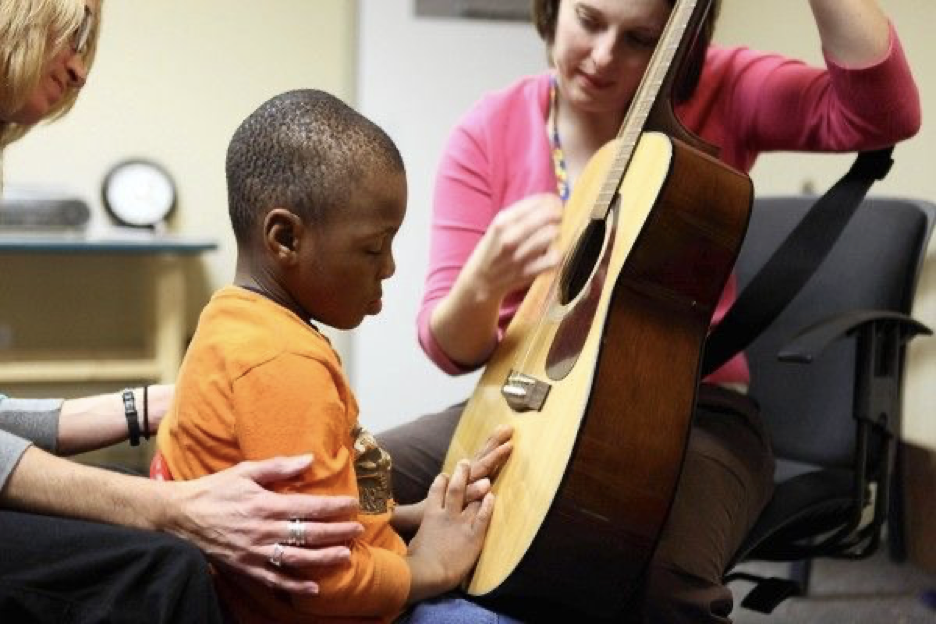

The basic objective of music therapy is to utilise music in improving patients’ overall wellbeing and assist them in achieving certain therapeutic goals. Music therapists work with a variety of people, including kids, adults, seniors, people with impairments, and people who are struggling with their mental health. To meet the needs and expectations of each person, they employ a wide variety of music-based interventions.
Music has a surprising impact on our cognitive abilities, especially when it comes to memory. It is a powerful instrument for evoking treasured memories because of its capacity to arouse strong feelings and leave enduring impressions. A timeless music has the mysterious power to take us back in time and spark vivid memories of bygone eras whenever we hear it. This amazing phenomena is a result of the way music activates several memory-related brain regions like the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. As a result, the art of melody turns into a priceless ally in organising and recalling memories, making it a useful tool for improving memory and supporting therapeutic efforts.
Beyond memory, music therapy has spread its therapeutic wings in many different areas, providing comfort and healing to individuals struggling to recover from strokes. Additionally, it extends a soft embrace to assist people dealing with trauma and the terrible aftereffects of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).

The following are some crucial elements of music therapy
1. Examination: Music therapists do an initial assessment of the client’s requirements, strengths, and limitations. A personalised music treatment plan is developed with the aid of this examination.
2. Active Music Creating: Active music-making is a component of music therapy, and entails the patient actively participating in musical activities like singing, playing an instrument, improvisation and creating. Making music encourages interaction and self-expression.
3. Therapeutic Targets: In accordance with the demands of the patient, music therapists establish specific targets. These objectives might include enhancing one’s ability to move, express emotions, remember things, speak clearly, interact with others, and generally feel good.
4. Emotional Control: Music has an immediate effect on emotions. In order to assist patients absorb and control their emotions, music therapists employ this emotional link. The use of music as a safe outlet for emotional expression and exploration.
5. Cognitive Stimulation: Music has the ability to activate different parts of the brain. This feature is used by music therapists to improve patients’ focus, recall, and cognitive function, particularly individuals with neurological problems.
6. Nonverbal Communication: Individuals who have trouble communicating verbally may employ music as a nonverbal form of conveying their feelings.
7. Sessions in Groups and One-on-One: Music therapy can be delivered in both group and private settings. Group sessions promote social contact and support, and one-on-one sessions enable tailored attention to particular needs.
8. Integrating Music Therapy with Conventional Therapies: Music therapy can enhance conventional therapeutic modalities like counselling and psychotherapy. By addressing emotional and psychological components of treatment through music, it can improve the overall effectiveness of the process.

The body of knowledge on music therapy has expanded, and the studies that have been conducted on it show that it is beneficial for a wide range of people and conditions. As a result, music therapy is now widely accepted in hospitals, clinics, schools, and mental health facilities.
Additionally, music has a significant impact on emotional resonance. Many different emotions can be evoked by various tunes and rhythms. A depressing piece can make you feel down, whilst an uplifting song might make you feel happy and excited. As a result of music’s capacity to synchronise with our emotional states and cause the production of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, we have an emotional response to it. These molecules are essential for controlling mood and emotion, underscoring the significant impact that music has on our emotional health. It is important to understand that individual differences in musical perception can be attributed to things like cultural background and life experiences. As a result, each person’s emotional reaction to a particular piece of music will be unique. It is possible to maximise the therapeutic advantages of music-based therapies by customising them to meet individual requirements and preferences by being aware of these variations.
The impact of music on memory is an enthralling area of study that demonstrates the power of music in changing our experiences and emotions. Music has a great deal of potential as a therapeutic aid, from its capacity to spark memories to its profound effects on brain health and emotional wellbeing. As we learn more about the complex relationships between music and the brain, it becomes clear that including music in daily activities might benefit our memory, ability to control our emotions, and general brain health.
Sources
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/8817-music-therapy
- https://www.apa.org/monitor/2013/11/music
- https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/therapy-types/music-therapy?amp
- https://jedfoundation.org/resource/how-music-can-improve-your-mental-health/#:~:text=your%20mental%20health.-,Music%20can%20be%20distracting%20and%20lower%20your%20stress,impact%20of%20depression%20and%20anxiety.
- https://www.aarp.org/health/brain-health/info-2020/music-mental-health.html
- https://www.verywellmind.com/surprising-psychological-benefits-of-music-4126866




