The question of whether love is merely an emotional experience or may be described scientifically is a difficult and contentious one. Love is a multidimensional phenomenon with emotional, psychological, and physiological components.
Love, a complicated and powerful feeling that has enthralled humans for millennia, has been extensively studied in the domains of art, literature, and philosophy. An opposing viewpoint, on the other hand, strives to explore the secrets of love using scientific methods and approaches. A detailed scientific analysis of love contends that love is fundamentally scientific, anchored in the complicated workings of the human brain and impacted by a variety of biological, psychological, and societal elements.
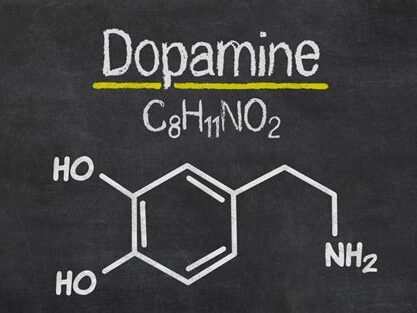
At its foundation, love has its beginnings in human biology. The human brain is crucial in the creation of love, with numerous areas and chemical processes contributing to its genesis. According to research, the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, oxytocin, and serotonin leads to emotions of love.
Dopamine, often known as the “pleasure chemical,” is linked to emotions of reward and motivation, whereas oxytocin, also known as the “bonding hormone,” encourages trust, social bonding, and attachment. Furthermore, the brain’s reward system and limbic system are important in reinforcing and sustaining feelings of love and connection.
Understanding why love has developed as a human feeling comes from the study of evolutionary psychology. According to the notion, romantic love in particular has evolved as an adaptive mechanism to promote healthy reproduction and the survival of children. The theory of sexual selection, put forth by Charles Darwin, explains why people who have characteristics that are seen favourably by potential partners are more likely to find a spouse and pass on their genes. So, in order to facilitate mate choice, encourage pair bonding, and improve reproductive success, love acts as a mechanism.
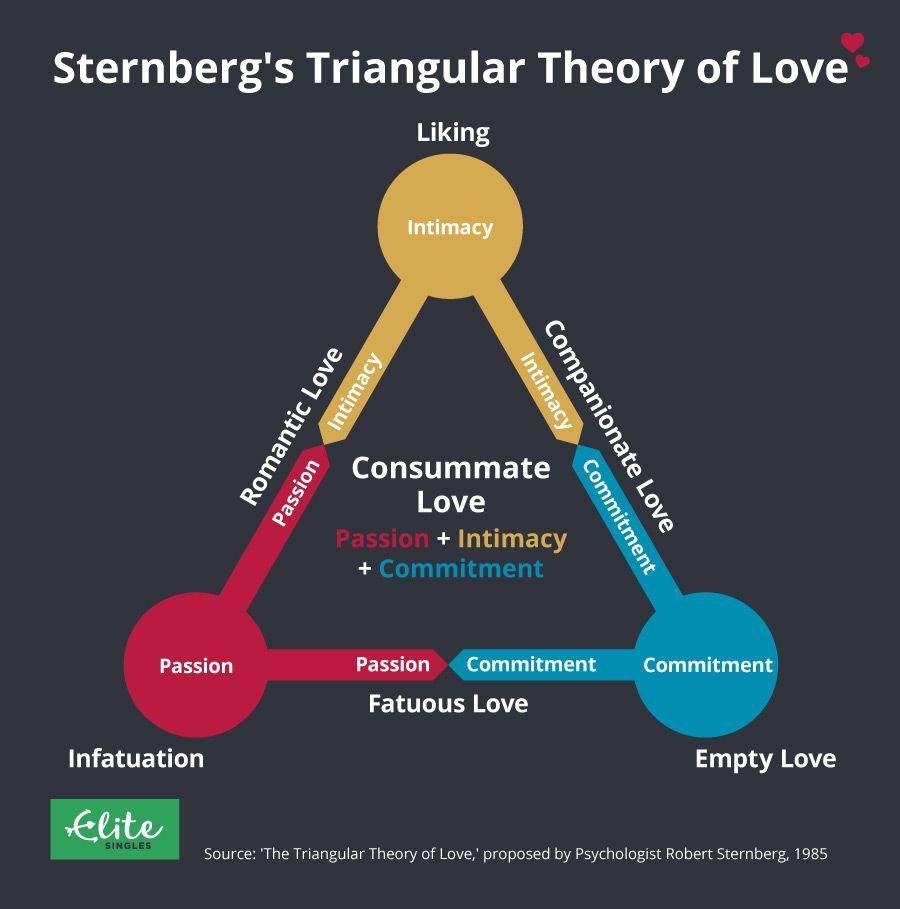
By exploring the cognitive and emotional processes involved, psychology also provides helpful insights into the psychological components of love. According to several theories, like Sternberg’s Triangular Theory of Love, there are three elements that make up love: closeness, passion, and commitment. These elements interact and change throughout time, influencing the many types of love that people feel. Attachment styles, which are ways relating to others established during early childhood events, are also investigated by psychological study. Attachment theory provides a framework to understand how individuals form emotional bonds and approach relationships based on their attachment styles.
Notably, Love is not solely a biological or psychological phenomenon; it is deeply intertwined with social and cultural factors. Sociological perspectives shed light on how love is influenced by societal norms, values, and expectations. Cultural variations exist in the ways love is perceived, expressed, and experienced. For instance, individualistic cultures may prioritise passionate romantic love, while collectivist cultures may emphasise companionate love and familial obligations. Societal institutions such as marriage and family also shape the expression and experience of love, further underscoring the social dimension of this emotion.
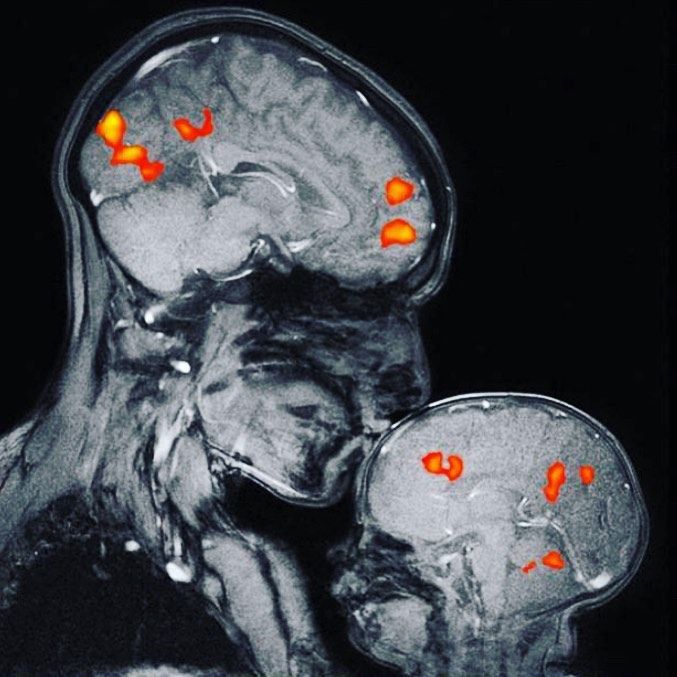
Furthermore, improvements in neuroimaging methods like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) have made it possible for researchers to see the brain in action while people feel love. These studies have demonstrated the role of particular brain areas in processing emotions, social cognition, and reward, including the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and insula. The scientific character of love is supported by neuroscientific research, which reveals the complex neuronal mechanisms underlying the experience of this emotion.
While love has historically been investigated via the lenses of art, literature, and philosophy, it may now be comprehended thoroughly through a scientific lens that includes biological, evolutionary, psychological, and sociological elements. The complex interaction of neurotransmitters, brain areas, evolutionary forces, psychological processes, and cultural factors all contribute to the creation and experience of love.
Taking a scientific approach to love helps us to comprehend its universality, discover its underlying mechanisms, and get a better understanding of this complicated and essential human emotion. While love is still a very personal and subjective feeling, knowing its scientific underpinnings broadens our grasp of its complexities and improves our capacity to research and appreciate this enthralling phenomena.
Sources
https://www.mountelizabeth.com.sg/health-plus/article/the-science-behind-why-we-fall-in-love#:~:text=The%20initial%20happy%20feelings%20of,us%20butterflies%20in%20our%20tummies.
https://wonderopolis.org/wonder/what-is-the-science-behind-love
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3537144/
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biological_basis_of_love
https://theanatomyoflove.com/faq/what-is-the-science-of-love/




